Arterial blood gases
Interpretation
Presenter
RNO Farman
Ullah
General Nursing , ICU
Speciality
,Post RN
B.Sc,N
.
DEPT: Medical ICU
Dated: 26
th
May,2023
Objectives
ABGS Sampling
ABGS Normal values
ABGS acidosis status(acid) and ABGS Alkalosis status(base)
Compensation
Mixed Disorder or Mixed picture
Types of Therapy for blood gases
Quiz
ABGS
The gases present in the blood of artery. The test perform for ABGS
Is ABGS test. ABGS test performed by ABGS machine
ABGS TEST
An arterial blood gases analysis (ABGS) measure the balance of potential hydrogen, oxygen , bicarbonate and
corbondioxide
in blood to see how lungs and kidneys work.
The process of analysis and monitoring of arterial blood gas (ABG) is an essential part of diagnosing and managing the oxygenation status and acid–base balance of the high-risk patients, as well as in the care of critically ill patients in the Intensive Care Unit.
In 1957, John
Severinghaus
developed the first blood gas analyzer
.
ABGS Machine
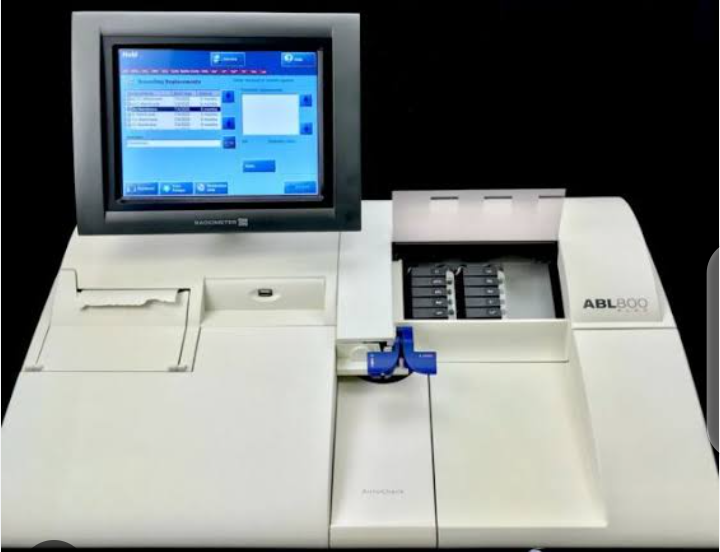
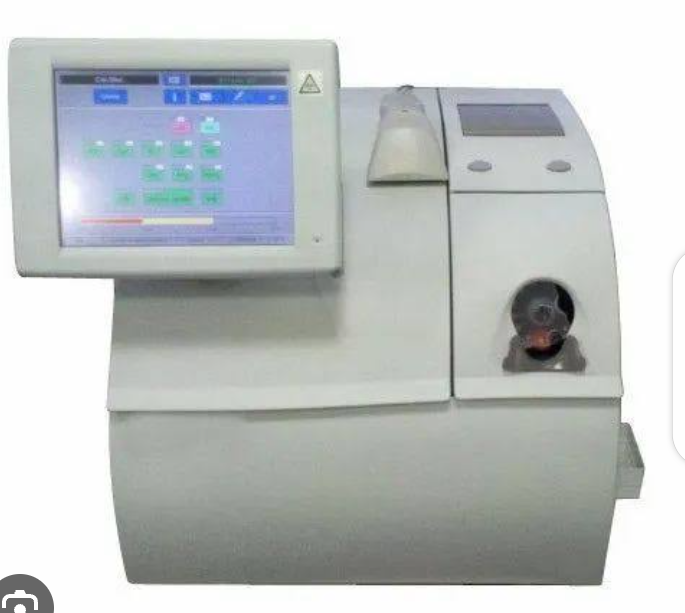


ABGS sampling
Sites :
Radial artery
Brachial artery
Femoral artery
IF
Arterial line
inplaced
Or
Femoral sheath
inplaced
Blood will be draw from lines
Brachial artery
Radial artery
Femoral artery
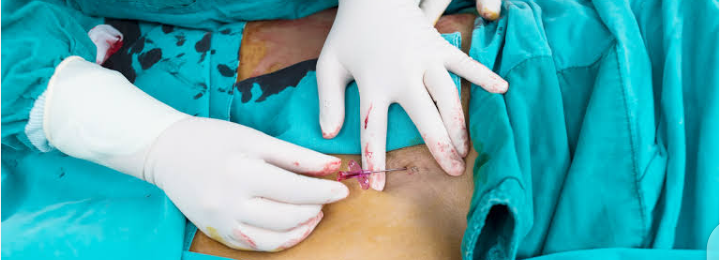
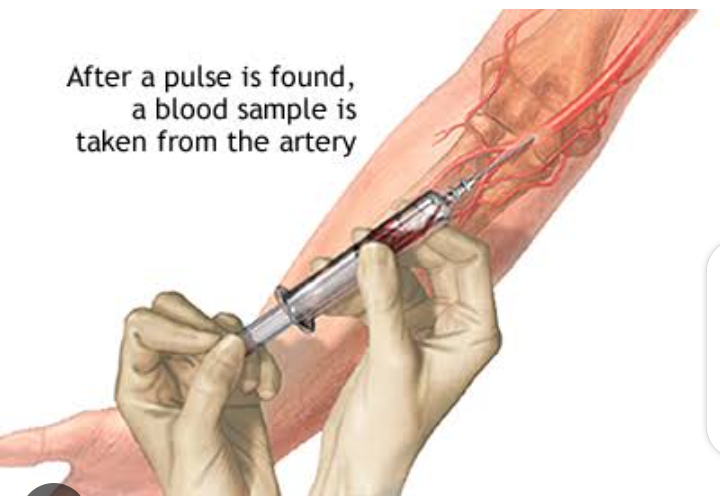
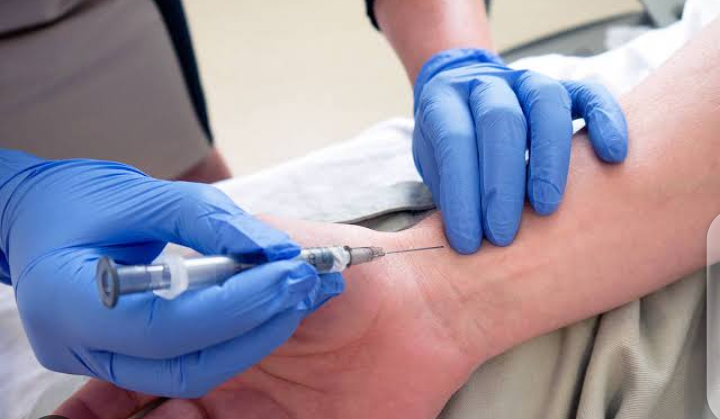
Figure 1
Figure 2
Arterial line
Femoral sheath
Figure 1
Figure 2
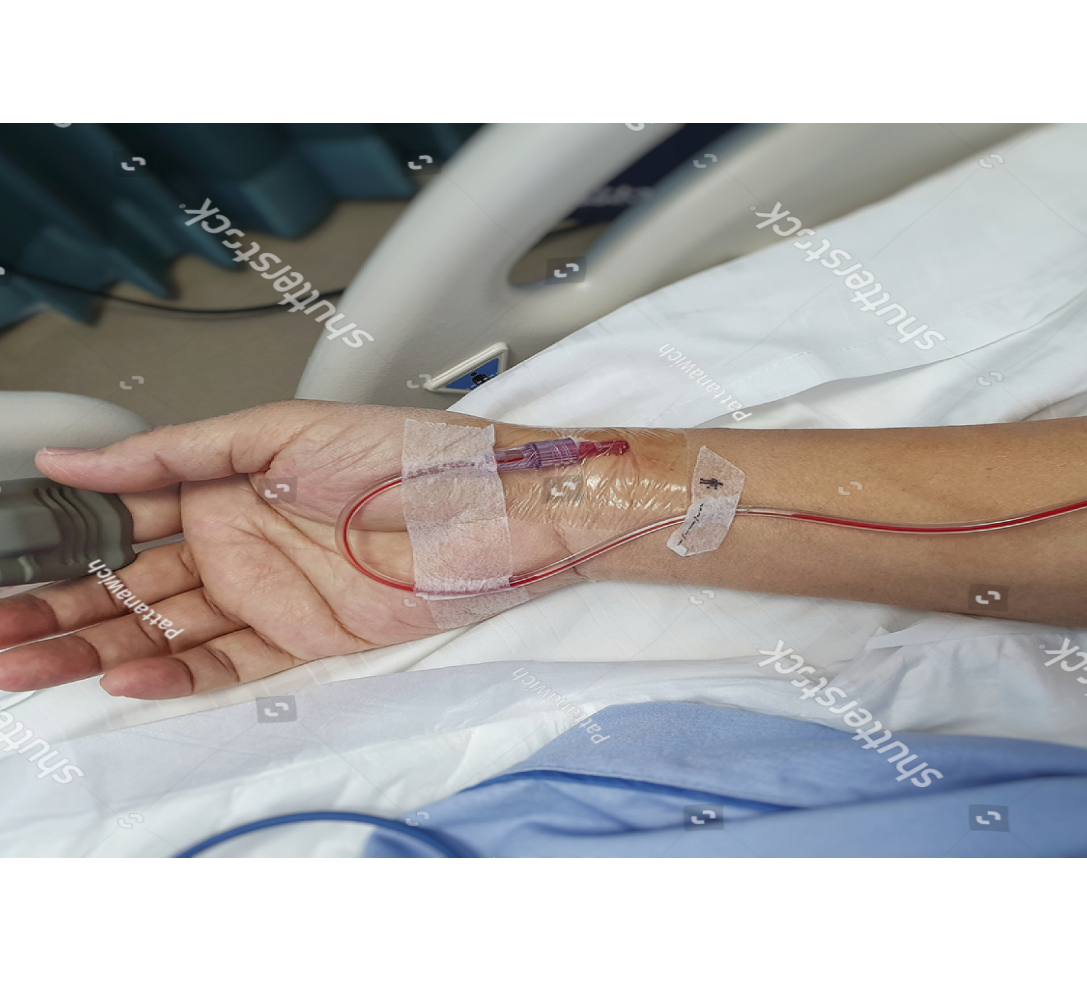
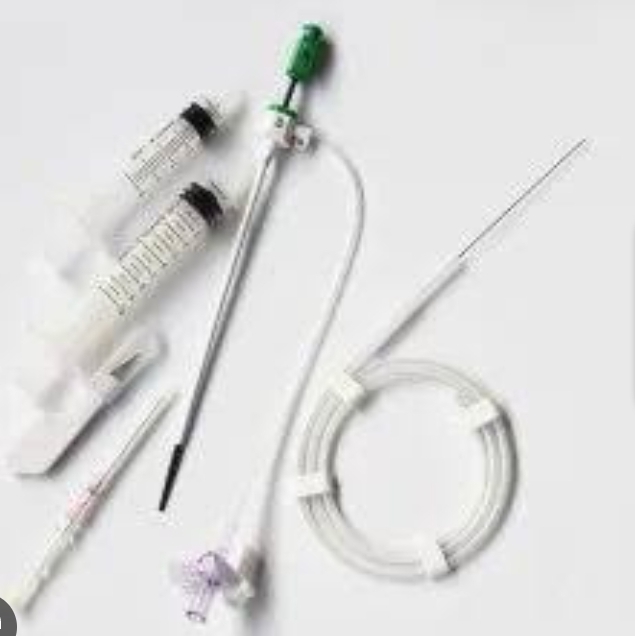
Potential Pre analytical Errors
During preparation prior to sampling
Missing or wrong patient/sample identification;
Use of the incorrect type or amount of anticoagulant
dilution due to use of liquid heparin;
insufficient amount of heparin;
Inadequate stabilization of the respiratory condition of the patient; and
Inadequate removal of flush solution in arterial lines prior to blood collection.
During sampling/handling
•
Mixture of venous and arterial blood during puncturing;
•Air bubbles in the sample. Any air bubble in the sample must be expelled as soon as possible after withdrawing the sample and before mixing with heparin or before any cooling of the sample has been done. An air bubble is a potential source of significant error and may seriously affect the pO2 value.
•Insufficient mixing with heparin.
During storage/transport
• Incorrect storage
• Hemolysis of blood cells
General Storage Recommendation
• Do not cool the sample.
• Sample analyze within 30 min.
• When analysis is expected to be delayed for more than 30 minutes, use of glass syringes and ice slurry is recommended.
During preparation prior to sample transfer
•Visually inspect the sample for clots.
•Inadequate mixing of sample before analysis.
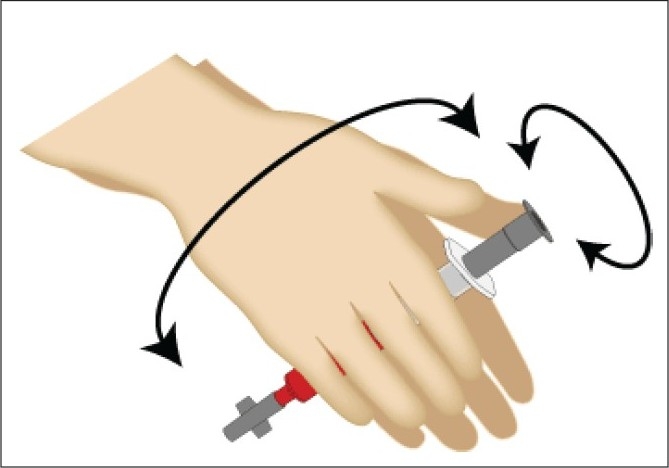
Insufficient mixing can cause coagulation of the sample. It is recommended to mix the blood sample thoroughly by inverting the syringe 10 times and rolling it between the palms as shown in Figure 3. This prevents stacking (such as coins or plates) of red blood cells.
Figure 3
Figure 3
Correct method of mixing of the arterial sample with the anticoagulant in two dimensions to prevent stacking of red blood cells.
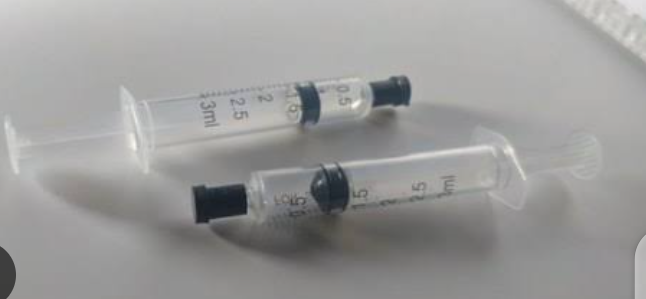
ABGS Syringes
There are two types syringes use
Modren
blood gases syringe
This syringe already heparinized with dry heparin and packed. should be checked
That how many IU/ML.
Normal range 50 IU/ML
Simple disposable Syringe
it is not heparinized . We should
take 0.05ml heparin then expelled heparin from 3cc syringe for heparinizing the syringe.
Figure 4
Modren
blood gases syringe
Modren
blood gases syringe
ABGS Normal
Rangesa
Analyzing three parameters are the most important while interpreting ABGS which are mentioned below.
(1) PH = 7.35 to 7.45
(2) CO2 = 35 to 45 mmHg
(3) HCO3 = 22 to 28
meq
/L
Spo2=95% to 100%
Po2 =80% to 100%
Step : 1
Acidosis
:
When PH reduces in ABGs from normal level (PH<7.35) is known as acidosis
PH
Alkalosis:
when PH increases in ABGs from normal level (PH>7.45) is known as
Alkalosis
PH
Step 2
Respiratory problems
When PH and CO2 inversely proportional to each other or in opposite direction if PH increases then CO2 will be reduced in ABGS and if PH reduces then CO2 will be increased in respiratory problems. (Absolutely lungs involved).
For example
Acidosis
normal
Respiratory Acidosis
PH=7.50
CO2=
20
HCO
3
=2
4
C
PH=7.
2
CO2=
6
HCO
3
=2
6
Respiratory Alkalosis
Alkalosis
Normal
Step 3
Metabolic problems
When PH and HCO3 directly proportional to each other or in same direction if PH increases then CHO3 will be increased in ABGS and if PH reduces then HCO3 will be reduced in metabolic problems (mainly kidneys involved).
For example
Acidosis
normal
Metabolic acidosis
PH=7.50
CO2=
40
HCO
3
=36
PH=7.21
CO2=
40
HCO
3
=1
4
Alkalosis
normal
Metabolic Alkalosis
Step 4
Compensation
Compensation is the mechanism by which the body copes with either acidosis or alkalosis
The main purpose of compensation is to normalize the PH of blood as persistent acidosis/alkalosis which causes damage to tissue and organs.
For example 1
(Respiratory problem with compensation)
Acidosis
Respiratory acidosis with
metabolic compensation
PH=7.59
CO2=
22
HCO
3
=14
PH=7.25
CO2=
55
HCO
3
=36
Alkalosis
Respiratory alkalosis with
metabolic compensation
Step 4
Example 2
Metabolic problems with compensation.
Metabolic acidosis with
Respiratory compensation
PH=7.57
CO2=
58
HCO
3
=38
Acidosis
PH=7.20
CO2=
20
HCO
3
=13
Metabolic alkalosis with
Respiratory compensation
Alkalosis
Step 4
There are two types of compensation
Partial
ompesation
Fully compensation
(1) Partial
compensation
:PH
will be increased or reduced from normal range (7.35 to 7.45)
for example
PH=7.55 Alkalosis
CO2=20
HCO3=12
(2) Fully
compensation
:PH
will be in normal range (7.35__7.40__ 7.45) .For example:
PH=7.43 Normal
C02=55
HCO3=40
Step 5
Mixed disorder or Mixed picture
Mixed picture is the mechanism in which both respiratory and metabolic problems will occur at a time.it means that both kidneys and lungs involved. focus should be on more problematic organ.
For example
(1) Metabolic acidosis
(2) Respiratory acidosis
Mixed picture with acidosis
PH=7.57
CO2=
23
HCO
3
=38
PH=7.20
CO2=
54
HCO
3
=14
Metabolic alkalosis
Respiratory alkalosis
Mixed picture with alkalosis
Acidosis
Alkalosis
Types of therapy for blood gases
There are two types of therapies invasive and non invasive therapy
Invasive therapy:
Invasive lines are those which are placed in body.
Naso
endo
tracheal tube
NETT
Oro
endo
tracheal tube
OETT
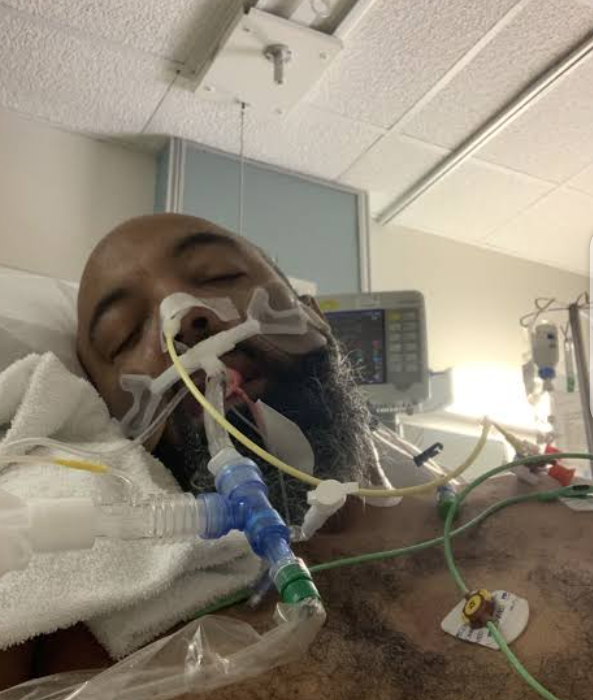

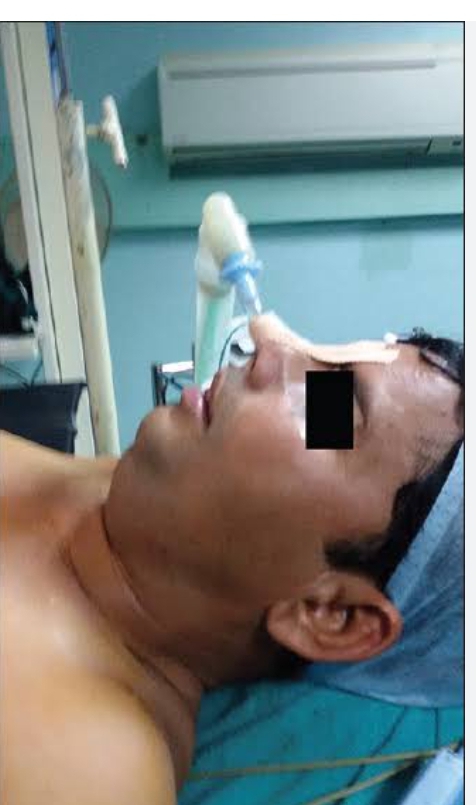
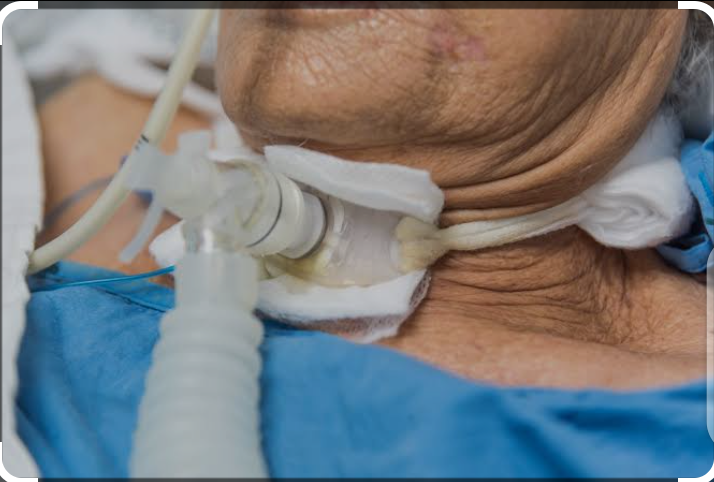
Non invasive therapy of
abgs
Those lines or Mask which are attached to body superficial are known as non invasive lines.
For example
NRM MASK BIPAP MASK LMA
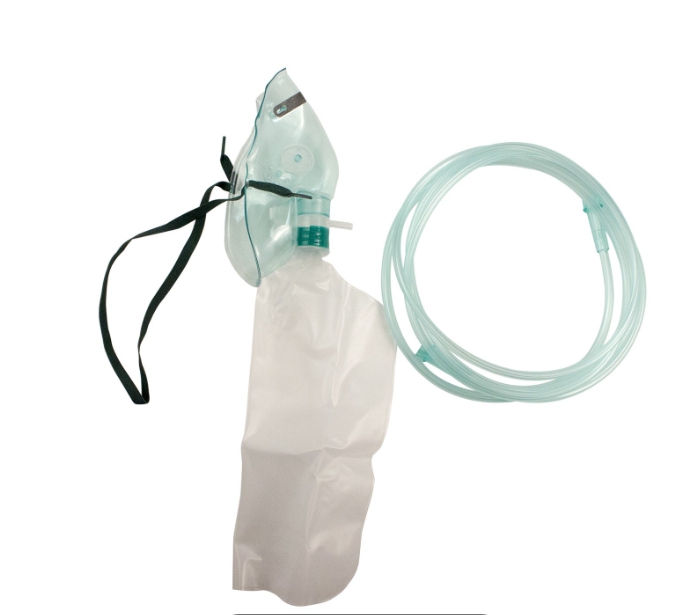
WISH ALL OF YOU ADVANCE HAPPY NURSES DAY




